-

Company
Product
ALUMINIUM MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINUM
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
ALUMINUM CORNER CRIMPING MACHINE
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS FOR ALUMINIUM COMPOSITE PANELS
NOTCHING SAWS
WEDGE CUTTING SAWS AND NOTCH CUTTING SAWS
MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
PVC PLASTIC MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
COPY ROUTERS FOR PLASTIC
END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
WELDING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
CORNER CLEANING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC PROFILES
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
GLAZING BEAD SAWS
AUTOMATIC MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
METAL MACHINES
MANUAL METAL SHEET BENDING MACHINE
MANUAL BENDING MACHINES
HYDRAULIC BENDING MACHINES
NON MANDREL BENDERS
PLATE BENDING MACHINES
BORDERING AND TRIMMING MACHINES
HORIZONTAL PRESSES
BELT GRINDING MACHINES
PIPE NOTCHING MACHINES
PIPE POLISHING MACHINES
LASER CUTTING MACHINES
PRESS BRAKES
VERTICAL TURNING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS
WOOD MACHINES
GLASS MACHINES
ROBOTICS SPECIAL MACHINERY
Service
Blog
Contact
Blog
- Home
- Blog
- BAR MACHINING CENTERS
- PROFILE MACHINING CENTERS
PROFILE MACHINING CENTERS

Profile Machining Centers – The Heart of Modern Aluminum Processing
Introduction
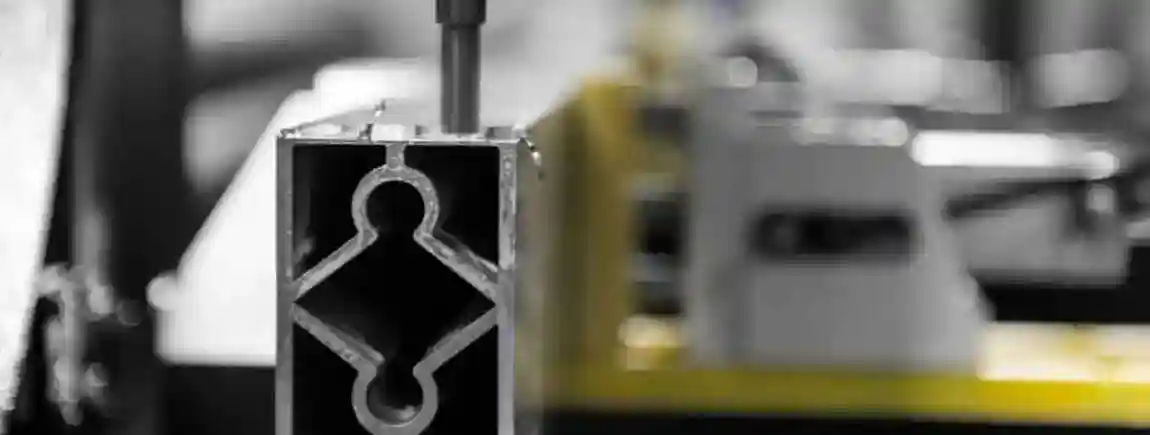
A profile machining center has become indispensable in modern industrial production. Whether in window manufacturing, door construction, facade engineering, mechanical engineering, or the automotive industry – wherever aluminum profiles, plastic profiles, or steel profiles must be processed with precision, these high-performance machines are used.
By combining CNC technology, multi-axis control, and automation, profile machining centers deliver maximum precision, efficiency, and flexibility. They replace a wide range of traditional standalone machines and enable machining operations that once required several manual steps and frequent retooling.
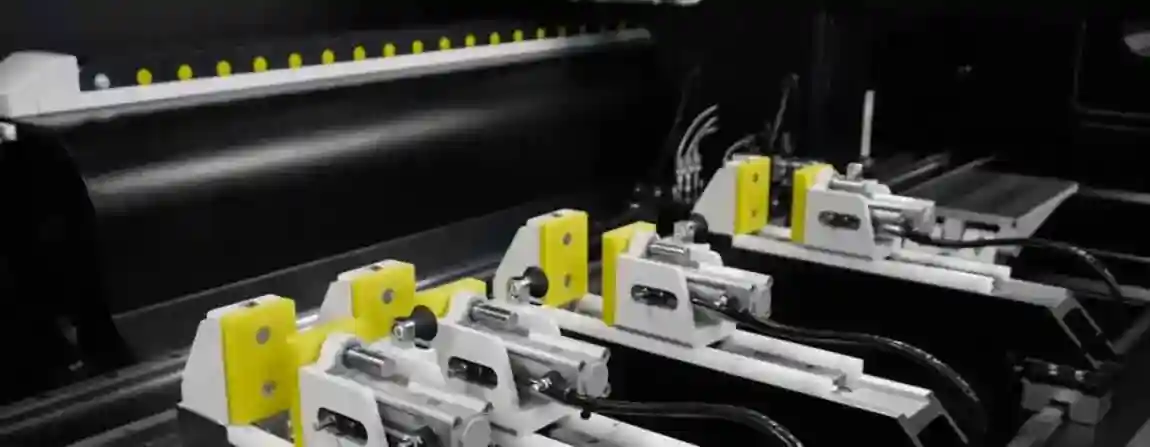
What is a Profile Machining Center?
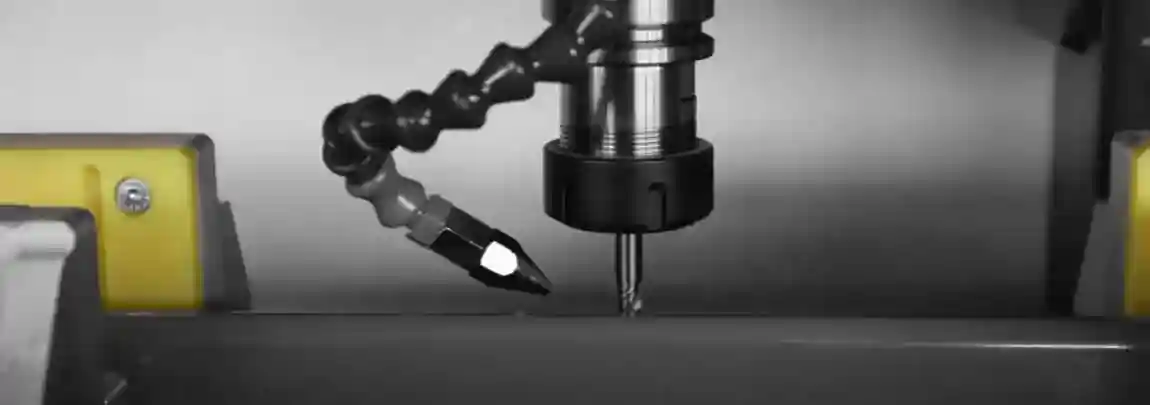
A profile machining center is a CNC-controlled machine tool designed for the complete processing of profiles – mainly aluminum, steel, or plastic. Typical operations that can be combined in a single system include:
-
Milling of contours, slots, recesses, and pockets
-
Drilling of through and blind holes
-
Thread cutting for screw connections
-
Sawing and miter cuts for precise joints
-
Groove milling for fittings and connecting elements
-
Cut-outs and slots for special constructions
-
Fitting machining for window and door systems
Thanks to advanced CNC control, even complex operations can be executed fully automatically. The machine follows programmed toolpaths with repeat accuracy down to a few hundredths of a millimeter – a decisive advantage over manual methods.
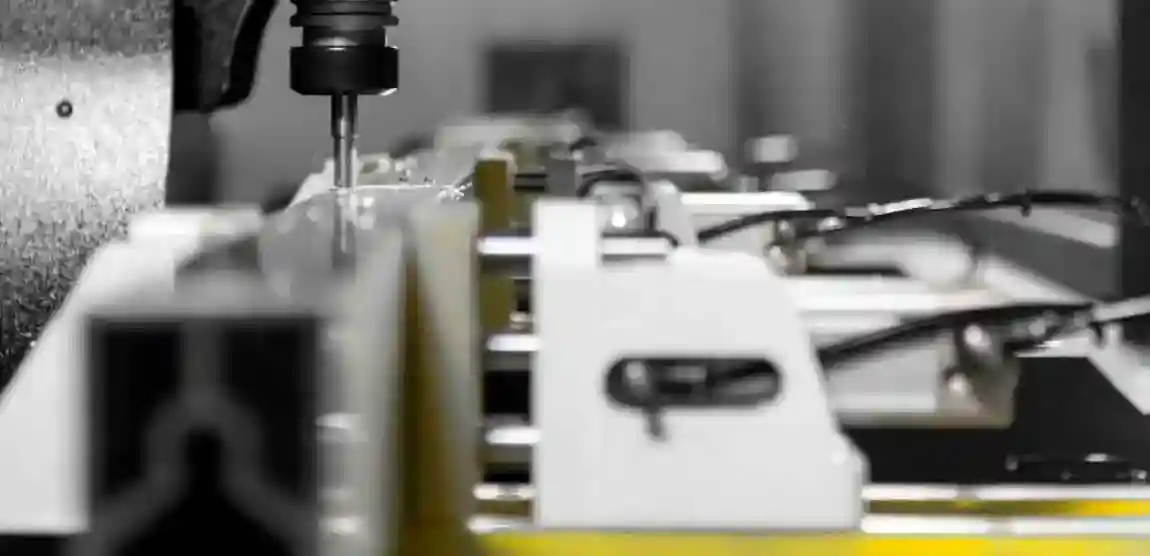
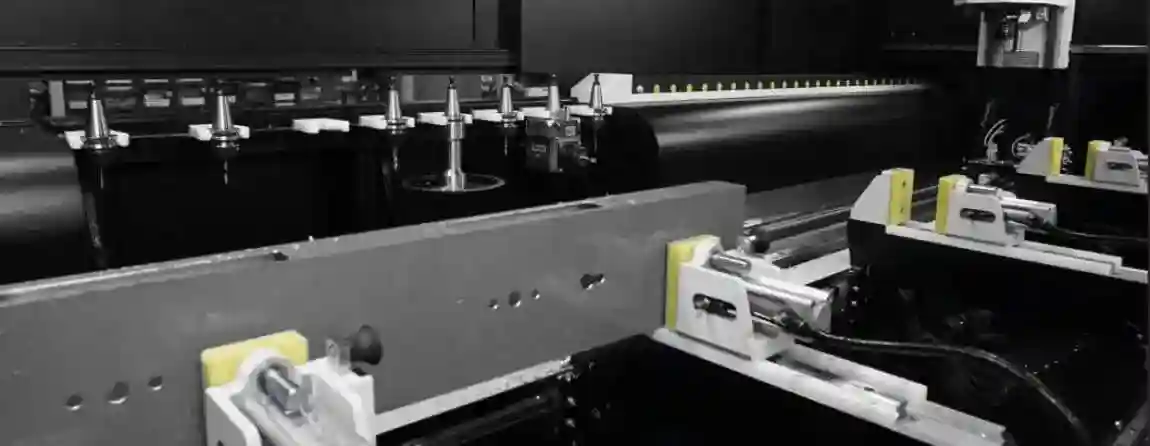
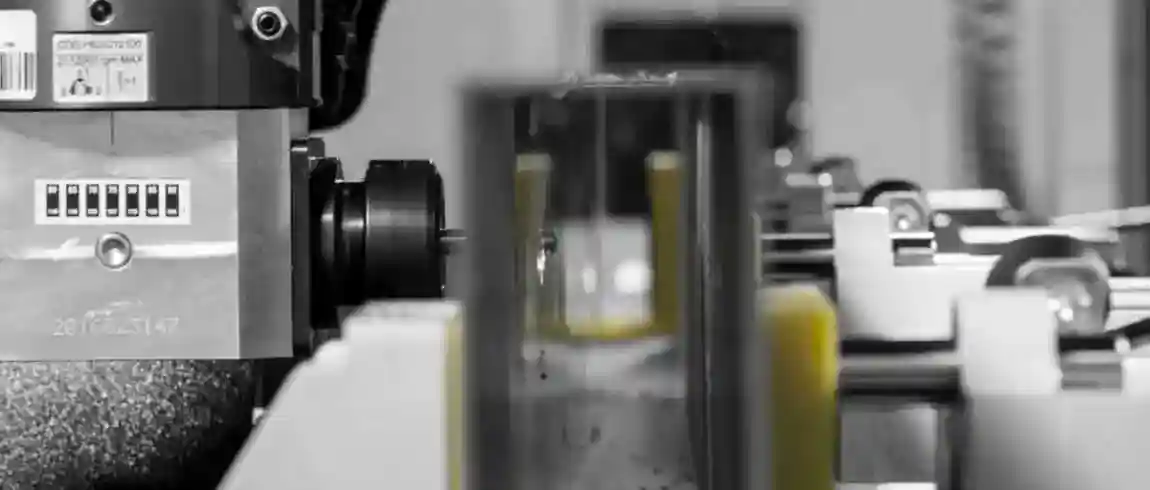
Technical Equipment of Modern Profile Machining Centers
Axis systems
-
3-axis: standard for basic aluminum profile machining
-
4- and 5-axis: for angled drilling, miter cuts, and complex geometries
-
6- to 8-axis high-end centers: for fully automated machining in all directions, often with rotation and swivel axes
Spindles
-
Servo-driven high-speed spindles up to 24,000 rpm
-
Air- or water-cooled systems for precise temperature control
-
Multi-spindle solutions for parallel operations
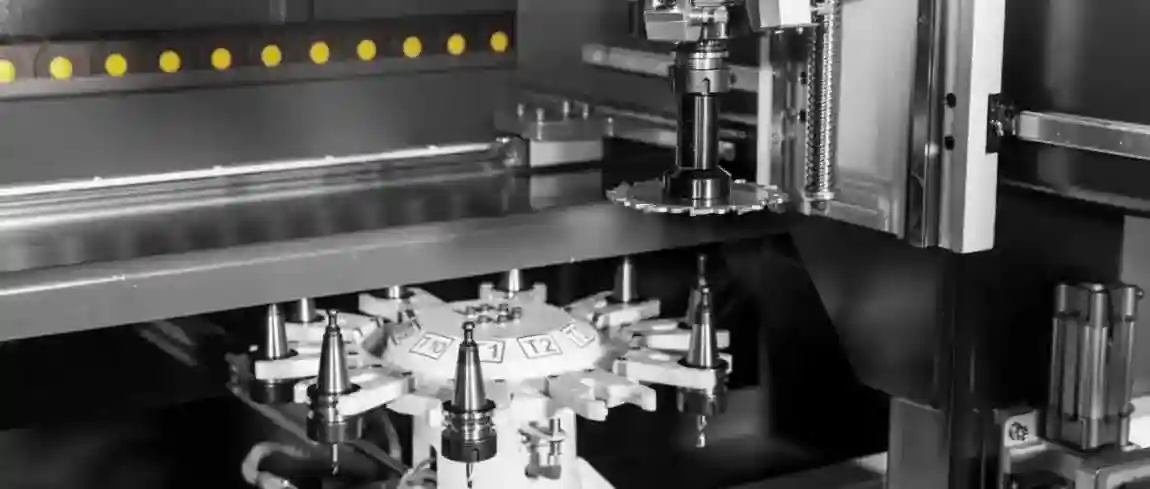
Tool changers
-
Automatic tool magazines with 12, 16, or 24 tools
-
Tool changes in seconds
-
Integration of saw blades, milling cutters, drills, and thread taps
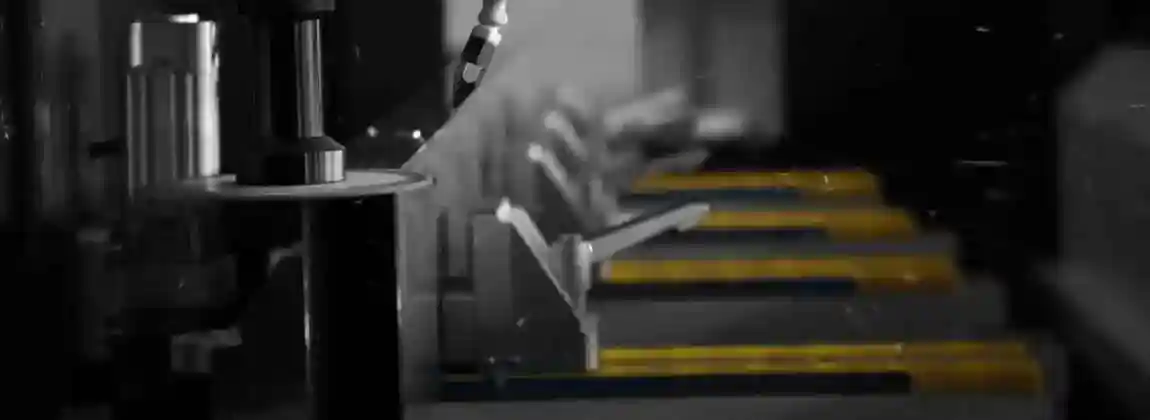
Clamping systems
-
Pneumatic and hydraulic clamps
-
Automatic adjustment to different profile sizes
-
Multi-clamping for series production
Extraction and cooling systems
-
Chip and dust extraction
-
Minimum quantity lubrication or coolant systems for extended tool life
CAD/CAM integration
-
Direct link to CAD software
-
Automatic conversion of drawings into CNC programs
-
Data transfer via network or cloud
Advantages of Profile Machining Centers
-
Maximum precision – accuracy within hundredths of a millimeter
-
Time savings – multiple operations in one clamping reduce setup times
-
Cost efficiency – less scrap, optimized material use, reduced labor costs
-
Flexibility – different profile sizes and materials on the same machine
-
Automation – seamless integration into digital production processes
-
Scalability – suitable for both small workshops and large factories
Application Areas
-
Window manufacturing: frame machining, fitting slots, drainage holes
-
Door construction: lock milling, precise miters
-
Facade engineering: large aluminum profiles for glass facades and special structures
-
Mechanical engineering: frames, structures, lightweight assemblies
-
Automotive industry: lightweight aluminum body and interior components
-
Furniture and lightweight construction: designer furniture, trade fair stands, modular systems
The Future of Profile Machining Centers
The demand for energy-efficient buildings, lightweight structures, and automated production is increasing worldwide. Profile machining centers are key to meeting these requirements.
Trends:
-
Industry 4.0 integration – machines communicate with production systems
-
Automated quality control – sensors monitor parts during machining
-
Robot integration – automated profile loading/unloading
-
Cloud-supported manufacturing – remote monitoring and real-time service
Conclusion
A profile machining center is more than just a machine – it is the core of modern production processes. Companies investing in this technology benefit from:
-
top precision
-
maximum efficiency
-
flexibility for custom solutions
-
a competitive advantage through automation
Whether in window and door production, facade construction, mechanical engineering, or automotive – profile machining centers are essential for the future of manufacturing.
- profile machining centers
- CNC profile machining center
- aluminum profile machining center
- CNC machining center for profiles
- aluminum profile processing
- CNC machine for aluminum profiles
- profile machining center windows
- profile machining center doors
- profile machining center facades
- milling aluminum profiles
- profile machining center buy
- used profile machining center
- profile machining center CNC 5 axis
- profile machining center CNC 8 axis
- automated profile machining center
 GERMANY
GERMANY ENGLISH
ENGLISH FRANCE
FRANCE SPAIN
SPAIN PORTUGAL
PORTUGAL