-

Company
Product
ALUMINIUM MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINUM
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
ALUMINUM CORNER CRIMPING MACHINE
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS FOR ALUMINIUM COMPOSITE PANELS
NOTCHING SAWS
WEDGE CUTTING SAWS AND NOTCH CUTTING SAWS
MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
PVC PLASTIC MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
COPY ROUTERS FOR PLASTIC
END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
WELDING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
CORNER CLEANING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC PROFILES
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
GLAZING BEAD SAWS
AUTOMATIC MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
METAL MACHINES
MANUAL METAL SHEET BENDING MACHINE
MANUAL BENDING MACHINES
HYDRAULIC BENDING MACHINES
NON MANDREL BENDERS
PLATE BENDING MACHINES
BORDERING AND TRIMMING MACHINES
HORIZONTAL PRESSES
BELT GRINDING MACHINES
PIPE NOTCHING MACHINES
PIPE POLISHING MACHINES
LASER CUTTING MACHINES
PRESS BRAKES
VERTICAL TURNING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS
WOOD MACHINES
GLASS MACHINES
ROBOTICS SPECIAL MACHINERY
Service
Blog
Contact
Blog
- Home
- Blog
- BAR MACHINING CENTER
- ALUMINUM PROCESSING MACHINING CENTERS
ALUMINUM PROCESSING MACHINING CENTERS

Everything You Need to Know About Aluminum Processing Machining Centers
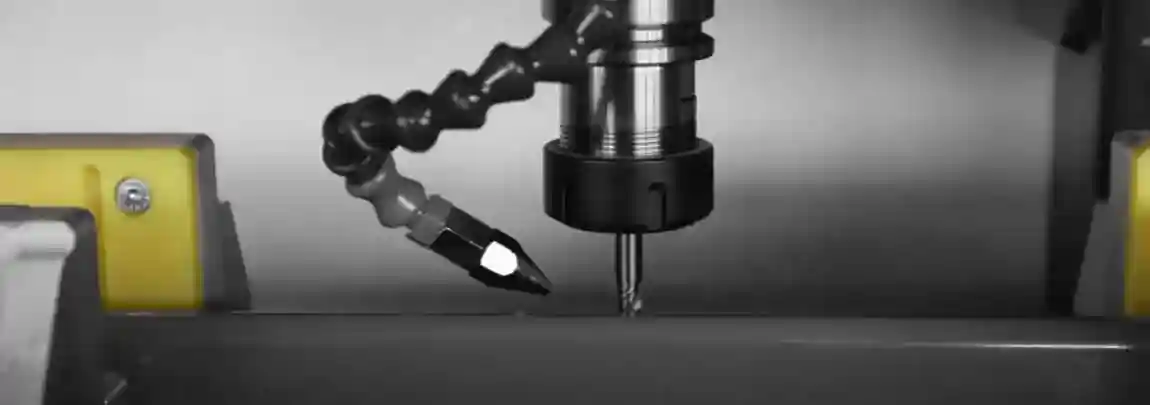
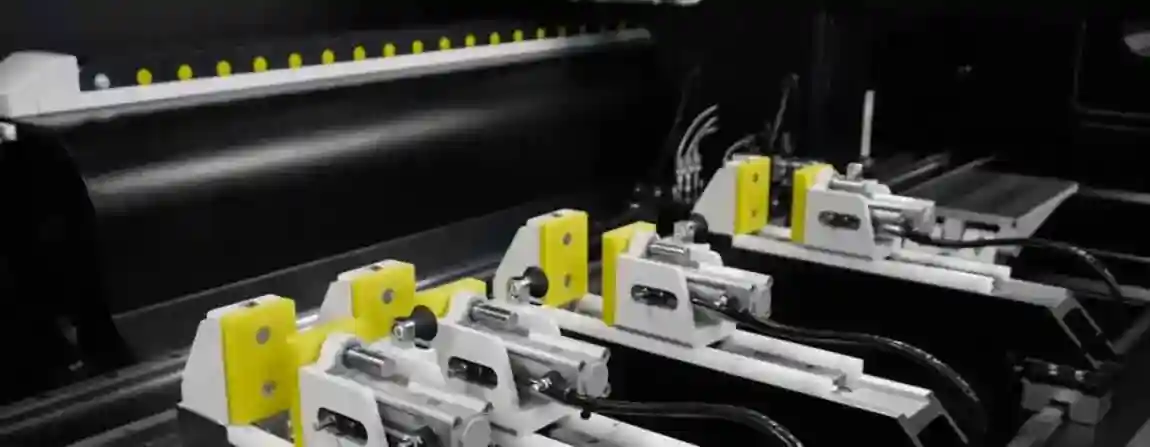
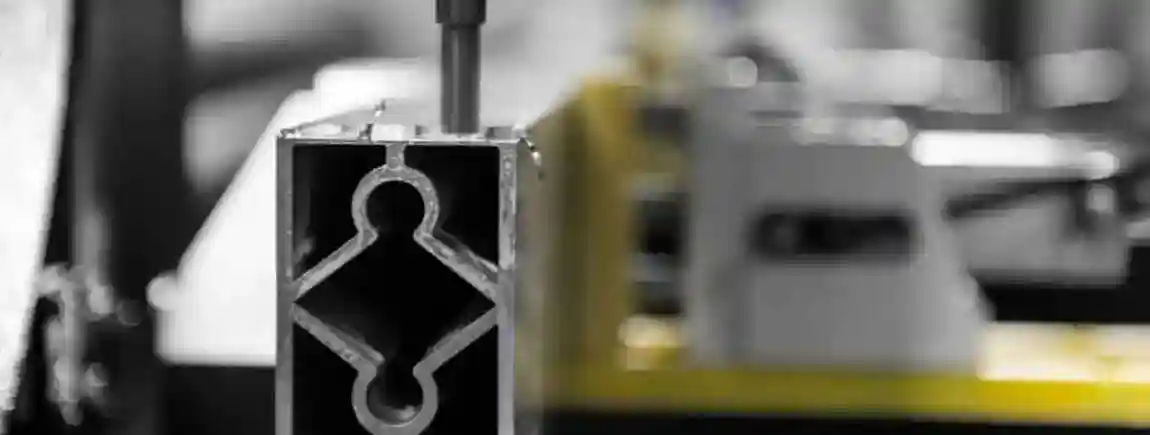
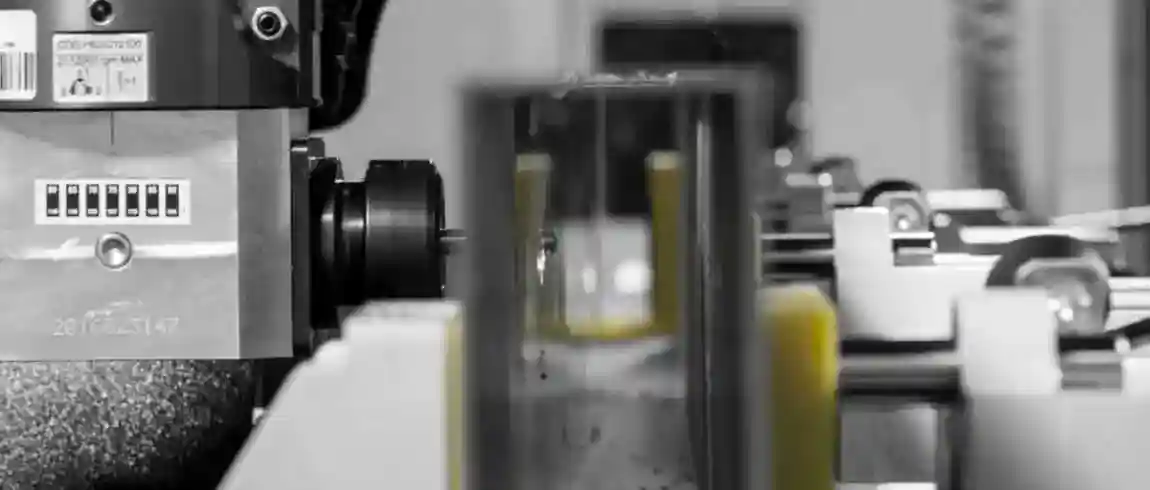
Aluminum is a vital material in various industries due to its lightweight, strength, and resistance to corrosion. To harness the full potential of aluminum, advanced machining centers are employed for its processing. These centers are equipped with state-of-the-art technology to perform precise, efficient, and versatile operations. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of aluminum processing machining centers, their types, benefits, and the future of this critical manufacturing process.
Introduction to Aluminum Processing Machining Centers
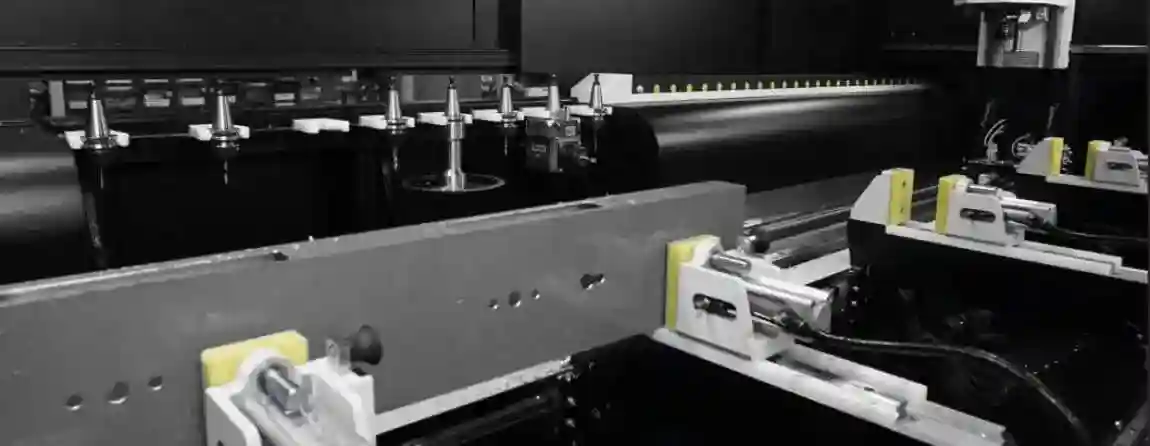
Aluminum processing machining centers are specialized machines designed to handle the unique properties of aluminum. These centers perform a variety of operations such as milling, drilling, cutting, and finishing. The goal is to produce aluminum components with high precision and quality, suitable for applications in automotive, aerospace, construction, and other industries.
Types of Aluminum Processing Machining Centers
There are several types of machining centers used for aluminum processing, each designed to handle specific tasks:
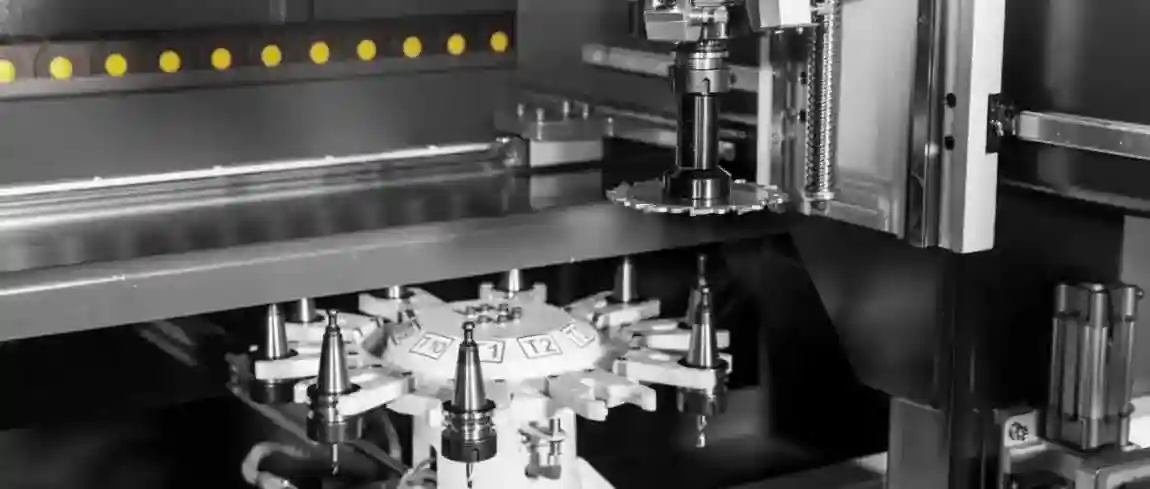
1. CNC Machining Centers
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining centers are highly versatile and capable of performing a wide range of operations. They offer precision, repeatability, and automation, making them ideal for high-volume production.
Vertical CNC Machining Centers (VMCs): These machines have a vertically oriented spindle and are commonly used for milling and drilling.
Horizontal CNC Machining Centers (HMCs): With a horizontally oriented spindle, these centers are suitable for heavy-duty operations and large workpieces.
2. 5-Axis Machining Centers
5-axis machining centers can move a tool or a part in five different axes simultaneously. This capability allows for the production of complex geometries and high-precision components. They are widely used in aerospace and automotive industries.
3. High-Speed Machining Centers
These centers are designed for rapid material removal and finishing. They use high spindle speeds and feed rates to enhance productivity and surface finish quality.
4. Hybrid Machining Centers
Hybrid machining centers combine traditional machining processes with additive manufacturing. This integration allows for the creation of complex parts with internal structures that would be impossible to produce using conventional methods alone.
Key Processes in Aluminum Processing
Aluminum processing involves several key operations, each requiring specialized techniques and tools:
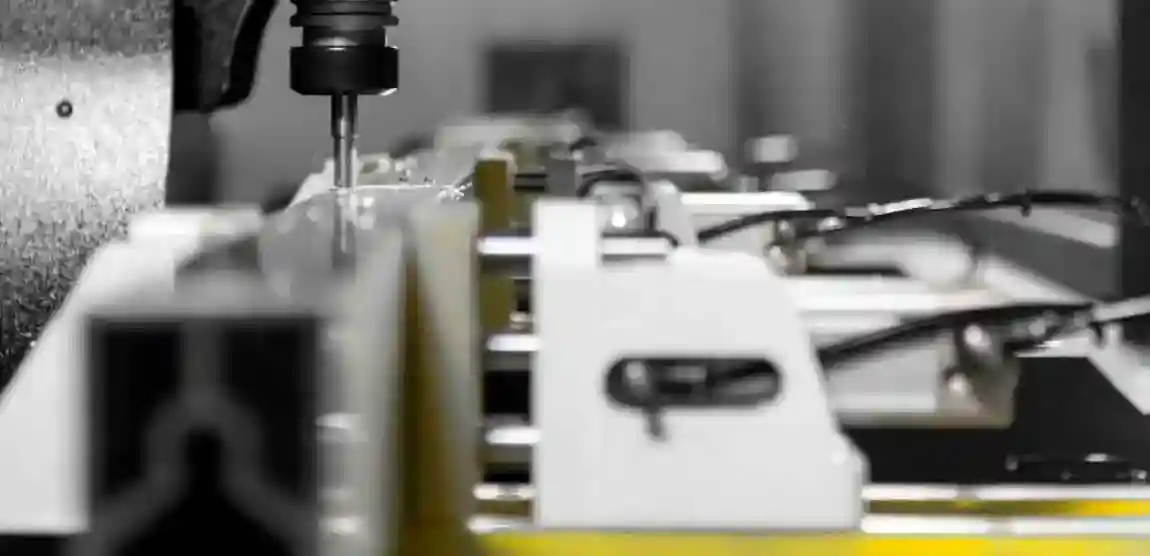
1. Milling
Milling is a machining process that uses rotary cutters to remove material from the workpiece. In aluminum processing, CNC milling is commonly used for creating complex shapes and contours.
Face Milling: Involves cutting a flat surface perpendicular to the axis of the cutter.
Peripheral Milling: Involves cutting along the sides of the workpiece to create intricate profiles.
2. Drilling
Drilling involves creating holes in the aluminum workpiece. CNC drilling machines provide high precision and can handle a wide range of hole sizes and depths.
3. Cutting
Cutting aluminum requires specialized saws and tools to ensure clean, precise cuts without deforming the material. Common cutting methods include:
Bandsaw Cutting: Uses a continuous band blade to make straight or curved cuts.
Waterjet Cutting: Employs a high-pressure jet of water mixed with abrasive particles to cut aluminum without generating heat.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the surface quality of aluminum parts. Techniques include:
Grinding: Removes small amounts of material to achieve a smooth surface.
Polishing: Produces a shiny, reflective finish.
Anodizing: Adds a protective oxide layer to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Benefits of Using Aluminum Processing Machining Centers
Employing machining centers for aluminum processing offers numerous advantages:
Precision: Advanced control systems and high-quality tools ensure precise and consistent results.
Efficiency: Automated processes reduce production time and labor costs.
Versatility: Machining centers can perform multiple operations, making them suitable for various applications.
Quality: High-speed and 5-axis machining centers produce superior surface finishes and complex geometries.
Challenges in Aluminum Processing
Despite its benefits, aluminum processing presents several challenges:
Heat Management: Aluminum's high thermal conductivity can lead to heat buildup, affecting tool life and surface quality. Proper cooling and lubrication are essential.
Tool Wear: Aluminum is abrasive, causing rapid tool wear. Using high-quality, coated tools can mitigate this issue.
Material Handling: Aluminum's softness makes it prone to deformation. Careful handling and clamping are necessary to maintain part integrity.
Future Trends in Aluminum Processing Machining Centers
The future of aluminum processing machining centers is shaped by technological advancements and industry demands:
Automation and Robotics: Increased use of robots and automated systems will enhance productivity and precision.
Smart Manufacturing: Integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) will enable real-time monitoring and optimization of machining processes.
Sustainable Practices: Focus on eco-friendly machining methods and materials to reduce environmental impact.
Advanced Materials: Development of new aluminum alloys with improved properties will expand the range of applications.
Conclusion
Aluminum processing machining centers are at the forefront of modern manufacturing, providing the precision, efficiency, and versatility needed to meet the demands of various industries. Understanding the types of machining centers, key processes, and benefits can help manufacturers make informed decisions and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market. As technology advances, these centers will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of aluminum processing.
- aluminum processing
- aluminum machining center
- CNC aluminum machining
- 5 axis machining center
- high-speed machining center
- hybrid machining center
- aluminum milling
- aluminum drilling
- aluminum cutting
- aluminum finishing
- aluminum machining challenges
- aluminum machining trends
- precision aluminum machining
- efficient aluminum processing
- automated aluminum machining
- smart manufacturing aluminum
- sustainable aluminum processing
- advanced aluminum alloys
- robotic aluminum machining
 GERMANY
GERMANY ENGLISH
ENGLISH FRANCE
FRANCE SPAIN
SPAIN PORTUGAL
PORTUGAL