-

Company
Product
ALUMINIUM MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINUM
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
ALUMINUM CORNER CRIMPING MACHINE
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS FOR ALUMINIUM COMPOSITE PANELS
NOTCHING SAWS
WEDGE CUTTING SAWS AND NOTCH CUTTING SAWS
MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
PVC PLASTIC MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
COPY ROUTERS FOR PLASTIC
END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
WELDING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
CORNER CLEANING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC PROFILES
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
GLAZING BEAD SAWS
AUTOMATIC MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
METAL MACHINES
MANUAL METAL SHEET BENDING MACHINE
MANUAL BENDING MACHINES
HYDRAULIC BENDING MACHINES
NON MANDREL BENDERS
PLATE BENDING MACHINES
BORDERING AND TRIMMING MACHINES
HORIZONTAL PRESSES
BELT GRINDING MACHINES
PIPE NOTCHING MACHINES
PIPE POLISHING MACHINES
LASER CUTTING MACHINES
PRESS BRAKES
VERTICAL TURNING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS
WOOD MACHINES
GLASS MACHINES
ROBOTICS SPECIAL MACHINERY
Service
Blog
Contact
Blog
- Home
- Blog
- PVC WINDOW MACHINE
- PVC WINDOW WELDING MACHINE
PVC WINDOW WELDING MACHINE

PVC Window Welding Machine: Technology, Applications, and Future Perspectives
A PVC window welding machine is at the heart of modern PVC window production. In this comprehensive expert guide, we explore the technology, functionality, application areas, historical evolution, benefits, costs, and future trends of this essential machine type. The content is written to be SEO-optimized and informative for both professionals and interested readers.
At various points, you will find natural references to Evomatec — a symbol of engineering precision and industry reliability.
Thanks to our many years of experience from numerous customer projects, we can ensure that inspections are always carried out with the utmost care in terms of quality and CE-compliant safety. (This core statement appears in several stylistic variations throughout the text.)
Understanding the Basics
Before delving into technical details, let us clarify a few essential terms.
-
PVC: Polyvinyl chloride – a thermoplastic polymer used in rigid (PVC-U) form for window profiles.
-
Window welding machine: A machine used to permanently join cut PVC profile ends through thermal welding, typically using a heating plate or mirror.
-
Welding process: In this context, mainly hot plate welding, also called “mirror welding.”
-
Seamless welding: A refined process minimizing visible joints.
-
Cleaning or finishing: After welding, joints are cleaned and smoothed for aesthetic perfection.
PVC window welding machines are often integrated into complete production lines that also include cutting saws, corner cleaning units, and automated transfer systems — forming the backbone of industrial PVC window manufacturing.
Historical Development of PVC Window Welding Technology
Early Manual Welding
Initially, PVC profiles were cut and manually pressed together using basic heating tools. This was a slow, labor-intensive, and inconsistent process.
Mechanization and Automation
By the mid-20th century, mechanical welding machines emerged — starting with single-head welders, progressing to double- and four-head systems that allowed multiple corners to be welded simultaneously.
This evolution marked the start of industrial PVC window production lines with integrated cleaning and automation.
Modern CNC and Seamless Technology
Recent years have brought massive advances:
-
CNC control for fully programmable cycles.
-
Seamless welding for invisible joints.
-
Integration into fully automatic lines with feeding, cooling, and cleaning stations.
-
Intelligent sensors and software for process optimization.
Today, PVC welding technology is highly advanced, combining reliability, automation, and consistent quality.
How a PVC Window Welding Machine Works
The Hot Plate (Mirror) Welding Process
This is the dominant process in PVC window manufacturing:
-
Heating phase – The profile ends are pressed against a heated plate.
-
Melting phase – The surfaces soften and reach the target temperature.
-
Welding phase – The plate is retracted, and the molten ends are pressed together under controlled pressure.
-
Cooling phase – The joint solidifies under maintained pressure.
-
Release – The finished welded corner is unclamped.
Accurate temperature, time, and pressure control are vital to achieve high-quality joints.
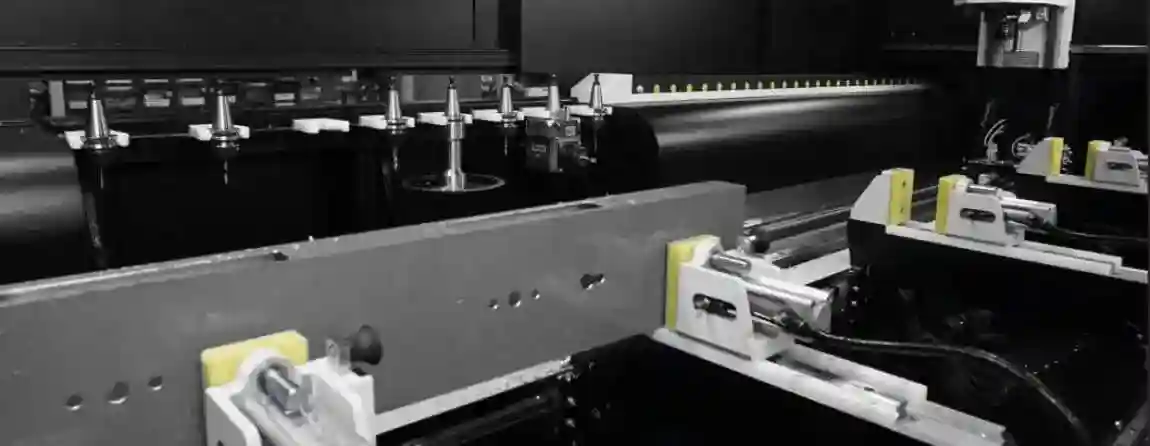
Main Components
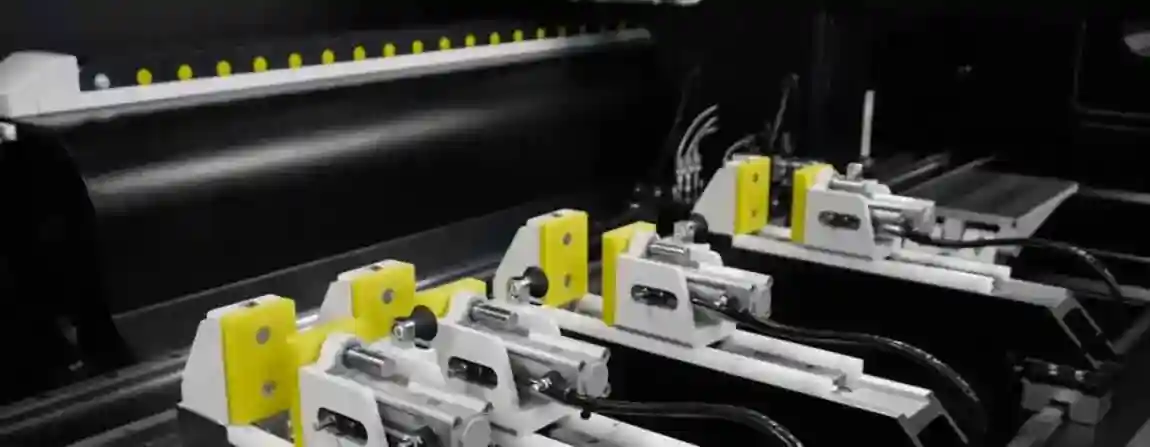
A typical PVC window welding machine includes:
-
Heating plates with Teflon coating.
-
Pneumatic or hydraulic pressure units.
-
Clamping fixtures for holding profiles.
-
CNC or PLC control system.
-
Temperature sensors and monitoring units.
-
Optional corner cleaning or polishing stations.
-
Integrated safety and CE-certified components.
Process Variants
-
Hot plate welding (standard)
-
Resistance welding for thin sections.
-
Ultrasonic welding in specialized plastics.
-
Seamless welding for high-end visual finishes.
Among these, hot plate welding remains the most robust and widely used technique.
Parameters Influencing Weld Quality
-
Cut accuracy – precise miters are crucial.
-
Temperature stability – consistent heat distribution is essential.
-
Time management – correct heating and cooling durations.
-
Pressure – must be perfectly adjusted to profile type.
-
Cleanliness – dirt or buildup can cause defects.
-
Material consistency – additives and coatings affect parameters.
-
Operator training and maintenance – skilled personnel ensure stability.
Typical Application Areas
Window and Door Manufacturing
The main industry using PVC window welding machines. They are employed for both frame and sash welding in high-volume production.
Hybrid Systems
Used for PVC profiles combined with aluminum or wood components, where the PVC segments are welded separately.
Small Workshops
Compact single-head machines are ideal for smaller operations or custom projects.
Research and Prototyping
Used for experimental designs and material testing in labs.
Renovation Projects
Occasionally used for retrofitting or repair applications in PVC window refurbishment.
Advantages and Challenges
Advantages
-
Excellent joint strength and tightness
-
High repeatability and productivity
-
Automation capability for large series
-
Improved aesthetics through seamless options
-
Cost-effectiveness over the long term
-
CE-compliant and safe operation
-
Easy integration into automated lines
Challenges
-
High investment cost for fully automatic models
-
Parameter calibration required for each profile type
-
Regular maintenance and calibration needed
-
Material variations may affect quality
-
Visible seam issues for high-design products
-
Large footprint for complete production cells
Despite these challenges, the benefits outweigh the drawbacks in industrial environments.
Real-World Examples
Fully Automated Four-Head Welding Line
A large factory uses a four-head CNC welding line integrated with cutting and corner cleaning modules. This setup allows all four corners to be welded simultaneously, greatly improving throughput.
Seamless Welding and Polishing
Premium systems combine welding and immediate corner polishing, creating an almost invisible joint.
Compact Workshop System
A small manufacturer operates a single-head hot-plate welder with a foot pedal for flexible small-batch production.
Thanks to our many years of project experience, we ensure that all inspections and calibrations meet the highest standards of CE-compliant safety and precision.
Customized Profile Programming
Factories producing unique profiles use machine-stored parameter sets for each profile geometry to ensure consistent results.
Retrofitted Machines
Older machines can be upgraded with new controls, sensors, and safety systems — significantly extending service life and quality assurance.
Machine Types and Comparison
| Type | Application | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-head welder | Small workshops | Flexible, low cost | Slower cycle time |
| Double/quad-head welder | Serial production | High throughput | Higher investment |
| Seamless welding system | Premium products | Invisible seam | Complex setup |
| Retrofitted systems | Existing lines | Cost-efficient | Limited by old mechanics |
Each configuration offers specific benefits depending on production scale and budget.
Economic Considerations
Investment Costs
Include the machine itself, automation modules, installation, and training.
Operating Costs
Cover electricity, consumables (Teflon sheets, heaters), maintenance, and staff.
Lifecycle Costs
Modern machines are designed for long service life, and proper maintenance minimizes total cost of ownership.
Profitability
Automated PVC welding systems typically pay off within a few years through higher productivity and reduced waste.
With extensive project experience, we ensure all inspections and validations meet CE-certified quality standards — ensuring investment safety.
Quality Assurance and Standards
-
European EN and RAL standards define performance criteria.
-
Factory Production Control (FPC) ensures ongoing compliance.
-
CE conformity under EU machinery directives.
-
Inspection and testing including visual checks, strength tests, and airtightness tests.
Through many years of project experience, Evomatec ensures that every inspection is carried out with maximum care for both quality and CE-compliant safety.
Integration and Automation
Modern factories integrate PVC welding machines into complete production lines with:
-
Profile feeding and buffering systems
-
Cooling and handling zones
-
Corner cleaning and finishing stations
-
Automated transfer and stacking systems
-
Data-driven process control and monitoring
Automation enhances consistency, minimizes human error, and improves traceability.
Thanks to our deep expertise, we ensure that every inspection and control cycle aligns with CE and quality management requirements — guaranteeing maximum production reliability.
Future Trends
-
AI-driven process optimization
-
Industry 4.0 connectivity
-
Energy-efficient heating systems
-
Smart sensors and self-calibration
-
Recyclable materials and sustainability focus
-
Modular and flexible machine architectures
These innovations are shaping the next generation of PVC window welding machines and production systems.
Key Criteria When Selecting a Machine
-
Production volume and throughput requirements
-
Profile types and geometry range
-
Number of welding heads and automation level
-
Budget and ROI expectations
-
Integration with existing equipment
-
Quality standards and appearance requirements
-
After-sales service, training, and spare parts availability
-
Compliance with CE and local regulations
Evomatec provides tailored advice based on long-term industry experience — ensuring inspections and commissioning are handled with precision and CE-compliant safety.
Conclusion
PVC window welding machines represent a vital technology in modern fenestration manufacturing. They enable durable, airtight, and aesthetically refined joints while ensuring consistent quality in industrial production.
Their evolution — from manual presses to intelligent CNC lines — demonstrates the sector’s drive toward precision, automation, and sustainability.
Future-oriented companies that invest in advanced systems today will gain long-term benefits in productivity, quality, and competitiveness.
Thanks to our extensive experience from numerous customer projects, we ensure that every inspection is carried out with the utmost attention to detail, always meeting CE-compliant quality and safety standards.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between single- and multi-head PVC welding machines?
Single-head machines weld one corner at a time and are suitable for small batches. Multi-head machines weld multiple corners simultaneously, ideal for large-scale automated production.
2. How important is profile cutting accuracy?
Extremely important. Any deviation in angle or dimension can compromise the welding quality and cause leakage or visible gaps.
3. Can all PVC types be welded?
No. Each PVC formulation requires fine-tuned temperature and time settings. Additives or coatings can affect weldability.
4. How often should machines be inspected?
Regularly — typically daily checks, weekly maintenance, and annual calibration. With Evomatec’s long-term expertise, each inspection ensures maximum CE-compliant safety and accuracy.
Free consultation available at www.evomatec.com
- PVC window welding machine
- PVC welding technology
- plastic window welder
- hot plate welding PVC
- multi head welding machine
- seamless welding system
- window production PVC
- window manufacturing welding
- CNC PVC welder
- welding quality control
- window fabrication automation
- inspection welding equipment
- investment window welding line
- window manufacturing technology
- process optimization PVC welding
 GERMANY
GERMANY ENGLISH
ENGLISH FRANCE
FRANCE SPAIN
SPAIN PORTUGAL
PORTUGAL